Ingenieros, geólogos, arquitectos y psicólogos trabajan en conjunto en el CIGIDEN para mejorar la forma en que el país se enfrenta a los desastres naturales desde un acercamiento totalmente interdisciplinario. El Centro alienta a los estudiantes para que se unan a este trabajo.
Archivo del Autor: ericksho
En Foco: Programa de Ingeniería Matemática
Dentro de Ingeniería Matemática y Computacional, puedes realizar investigación de clase mundial por medio de la modelación matemática, análisis, desarrollo de algoritmos numéricos de alto rendimiento y su implementación computacional para diversos problemas interdisciplinarios: desde el diseño nuevos materiales en ingeniería, sistemas biológicos o financieros, hasta el mismo análisis del Big Bang.
La ingeniería mecánica es la rama de la ingeniería que se dedica a la conversión de energía y al diseño, producción y operación de máquinas, mientras que la ingeniería metalúrgica se centra en la extracción, aleación y fabricación de metales. El Departamento de Ingeniería Mecánica y Metalúrgica (DIMM) de la UC tiene siete laboratorios de investigación y cuenta con un equipo de 14 académicos. http://ipre.investigacion.ing.uc.cl/wp-admin/post-neRosario Contesse y Mariana Valle, consejeras académicas de pregrado en 2015 y 2013, respectivamente, aclaran las incertidumbres que tienen los alumnos de pregrado al momento de incursionar en investigación. Este invento innovador consiste en una pila de combustible sólida que tiene la capacidad de usar combustibles como hidrocarburos líquidos o gaseosos para poder generar energía en forma de electricidad. Ya completo este nuevo número del Journal I3: Investigación, Interdisciplina e Innovación, no dejo de sorprenderme con el tremendo entusiasmo de alumnos y profesores que intentan transmitir la relevancia de la investigación en pregrado. Son justamente ellos, nuestros ahora alumnos, los que nos sucederán en algún momento, más tarde o más temprano, para seguir avanzando en este proceso infinito de crecimiento del ser… Nicole Blin, Victoria Sandoval, Francisco Suárez, Felipe Victorreo, Carlos Bonilla, Jorge Gironás, Sergio E. Vera, Waldo Bustamante, Vicky Rojas, Pablo Pastén. Abstract Green roofs are technological solutions that integrate vegetation into infrastructures to reach benefits such as the reduction of rooftop runoff peak flows. The proper performance of a green roof depends on its substrate, which is an artificial media that has an improved performance compared to natural soils. Therefore, it is very important to investigate the substrate properties to characterize the behavior of a green roof, and to optimize its performance. This work investigates the hydraulic properties of three substrates commonly found in green roofs, corresponding to Las Brujas, Verde Activo and Jardinsen, by means of drainage experiments and numerical simulations. The drainage experiments consist in substrate columns that are saturated with water and then drained by fixing different pressure heads at the bottom of the column. These experimental data enables the determination of the water retention and hydraulic conductivity curves of each substrate by inverse modeling using the Hydrus 1D software. It was concluded that, among the three substrates used in this investigation, the Jardinsen substrate retained a larger amount of water. Therefore, we recommend the use of this substrate to reduce surface runoff of storms with small return period. Nicolás Schmidt, Arshia Cont, Jean-Louis Giavitto. Abstract The problem of preservation through time of interactive music pieces has always been present in this field of contemporary music. Because of the size, versatility and computational power of the UDOO minicomputer, INRIA’s MUTANT team has decided to compile a version of the Antescofo software in order to conserve these musical pieces. However, because of the digital signal processing architecture of the software, a nonoptimal performance for the interpretation of real time pieces was observed. In this article, we present a new version of Antescofo that changes the signal processing paradigm from an architecture of a message passing system between Antescofo and external patches, to an architecture that integrates the Faust digital signal processing library. This research is based on the perform of profiling tests for both versions, with the aim of seeing if the new architecture is actually better in terms of performance for real time applications than the older version. The methodology used was to compare both versions performing the interactive music piece “Anthèmes 2” from Pierre Boulez and the comparison of the execution times of the digital signal processing process. The new architecture showed an improvement of 46%. The results exposed suggest that the technical resources of the UDOO platform are enough to run a version of Antescofo, allowing this way to preserve interactive musical pieces through time. Raimundo Gillet, Angélica Fierro, José Ricardo Pérez-Correa, Loreto M. Valenzuela. Abstract Polyphenols are a family of chemical compounds widely distributed in plants. Their antioxidant, antiviral, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties have attracted the interest of the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Therefore, their optimal extraction from plant material is an active research topic in process engineering. Polyphenol compounds contain aromatic rings and alcohol groups in their structure, leading to a hydrophilic behavior in most cases. Hence, pressurized hot water is a viable, safe and environmentally friendly solvent for their extraction. It is possible to study the affinity of polyphenols for water as a first approach to understand their aqueous solubility at different temperatures and pressures. Equilibrium affinity between compounds is represented by their intermolecular attraction or repulsion; therefore molecular dynamics simulations could be useful to better explain the solubility of polyphenols in water. One of the simplest polyphenol molecules is benzoic acid, which implies that its molecular dynamics simulations should be simple to perform. Also, there is a large amount of experimental data on the literature to compare its solubility with the simulation results. The purpose of this study was to explore the applicability of molecular dynamics simulations in predicting the solubility of benzoic acid in water at different temperatures by analyzing interatomic distances and some of its equilibrium properties. Molecular dynamics simulations were carried out at isothermal-isobaric conditions using the NAMD v2.9 software, and the interaction between water and benzoic acid was analyzed at different temperatures. The effects of intermolecular interactions were studied by means of an analysis of energies, hydrogen bonding and radial distribution functions (RDF), once the equilibrium was reached, and the results were compared with experimental solubility data. It was observed that the average amount of hydrogen bonds increases with increasing solubility until it reaches a maximum value. Omar Seguel, Patricia Galilea. Abstract The intensive growth of Santiago, the continuous increase in motorization rates and the increase on social inequality in the country have resulted in the setting of a strongly segregated city with unequal patterns of mobility among different sectors of the population. The objective of this article is to contrast the situation faced by the various sectors of the population inhabiting the Chilean Capital by studying several demographic, socioeconomic, urban and mobility patterns for eight municipalities that are located on the periphery of Gran Santiago. First, we studied how housing policy, the absence of a urban regulation policy, the using of free market as the only tool for valuing, and distributing the urban land and the liberalization of the transport system, derived in diverse urban development processes that explain the current expansion and segregation within Gran Santiago. Subsequently, the inequalities in urban mobility patterns in different municipalities were studied and contrasted. The results indicate huge differences on how the people from different districts move within the city. Therefore, it was concluded that the inequality in urban mobility creates an urban configuration that benefits upscale sectors and increases the divergence within the city. These results emphasized the need for creating transport and urban planning policies to remedy the current unequal configuration of the city. 
En Foco: Departamento de Ingeniería Mecánica y Metalúrgica
Investigación en pregrado: investigación como herramienta para el aprendizaje
Ícaro: Bloom Energy, energía para el futuro
Editorial: con la mirada en el 2030
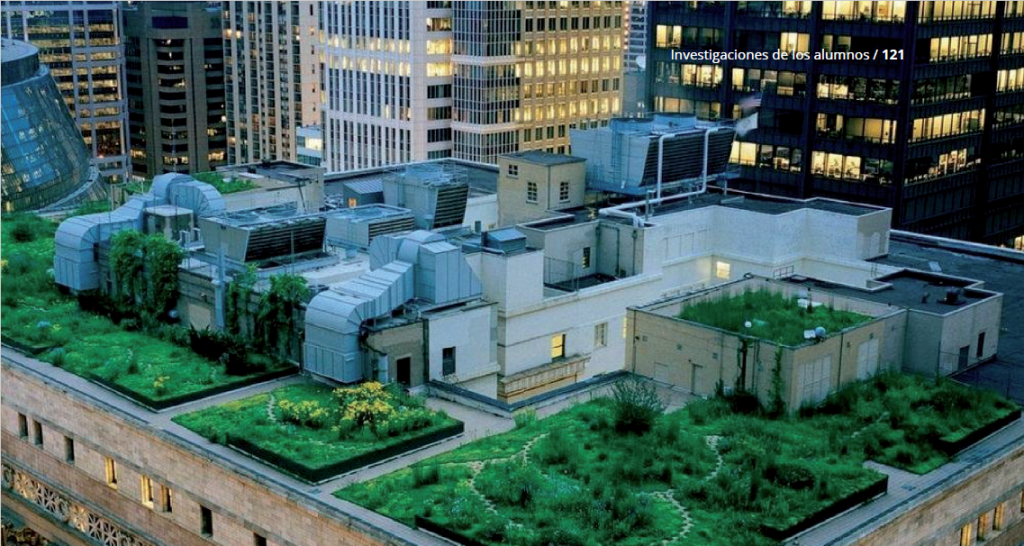
Leer más…Determination of hydraulic parameters of green roofs through drainage experiments and inverse modeling with Hydrus 1D
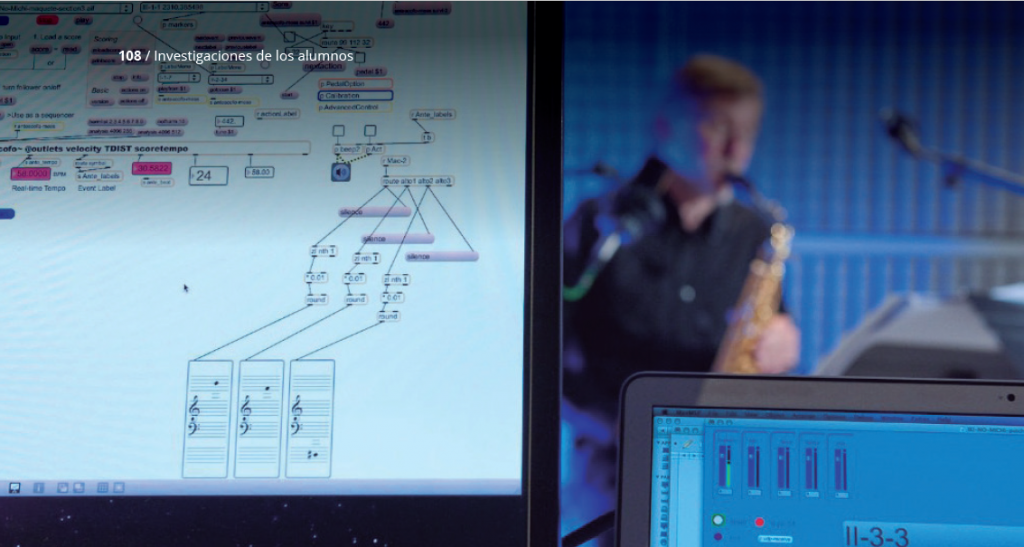
JI3 2016, number 6, pages 121-131.First steps toward embedding real-time audio computing in Antescofo
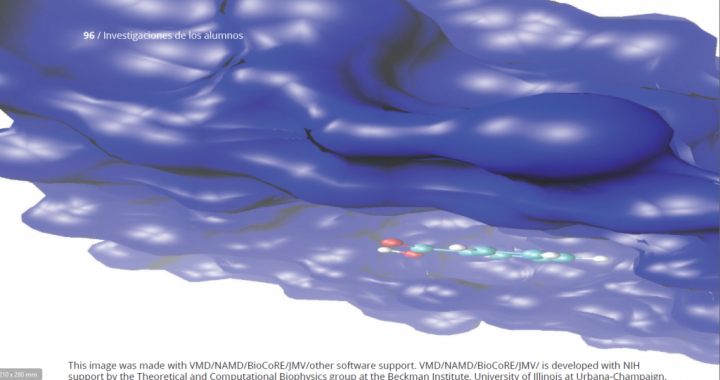
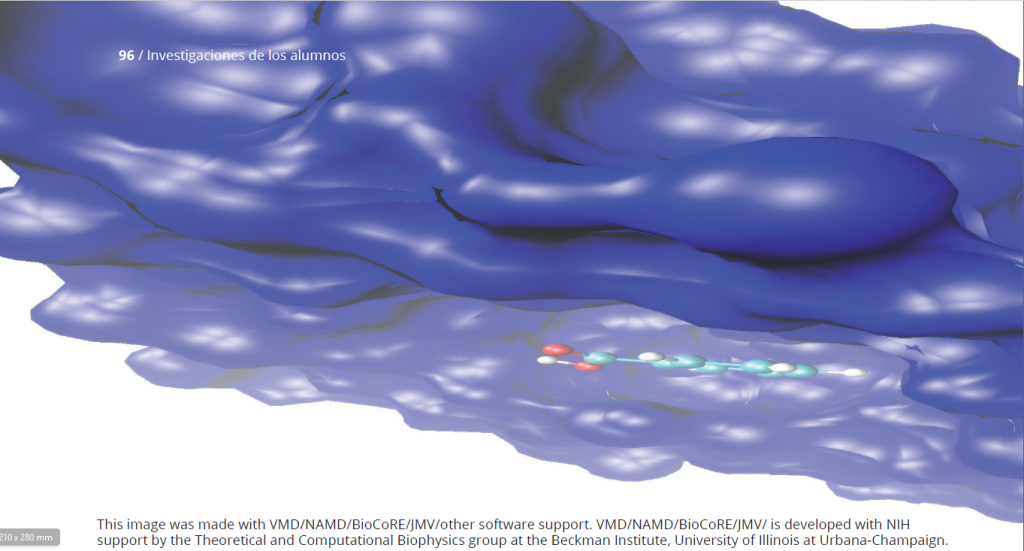
JI3 2016, number 6, pages 108-120.Molecular dynamics simulation for a mixture of benzoic acid in water: Relation between interatomic positions and solubility
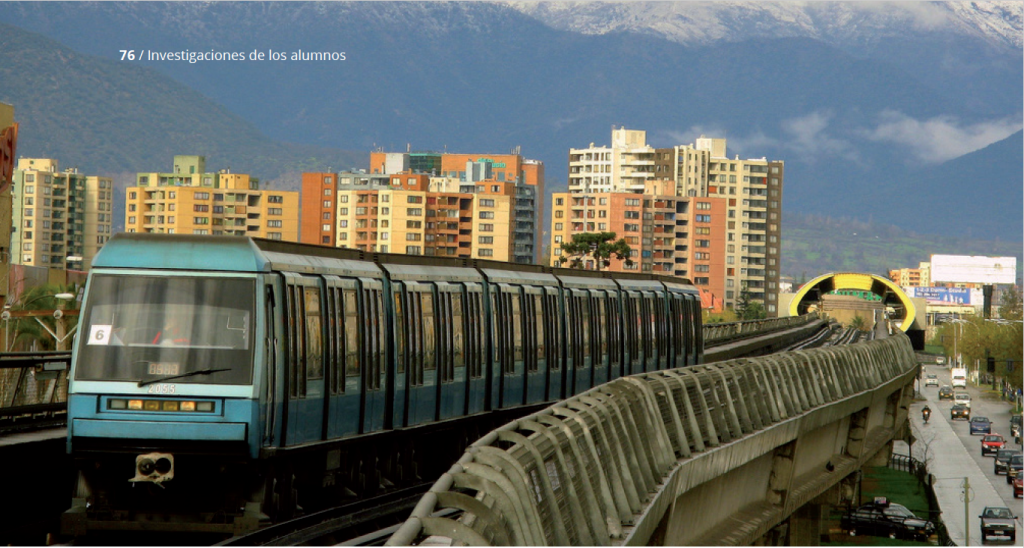
JI3 2016, number 6, pages 96-107.Socio-spatial segregation and urban mobility in Santiago
JI3 2016, number 6, pages 76-95.